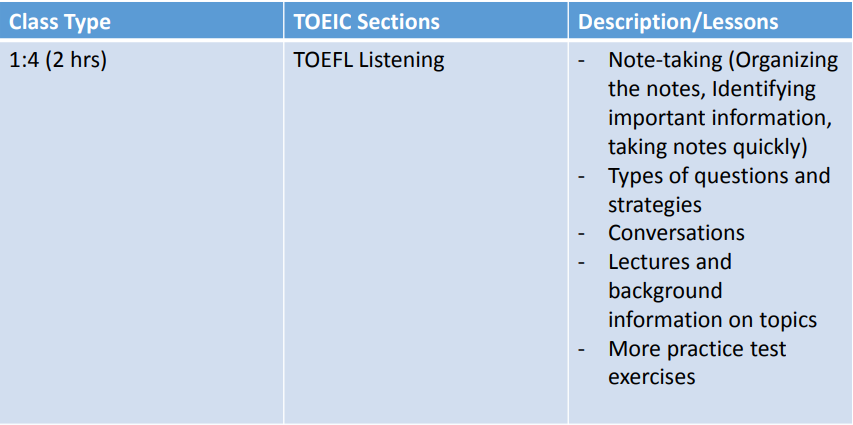
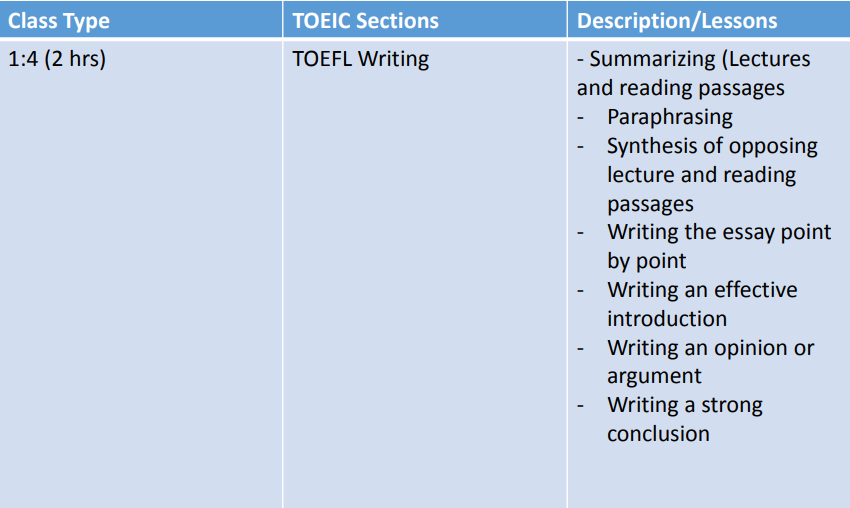
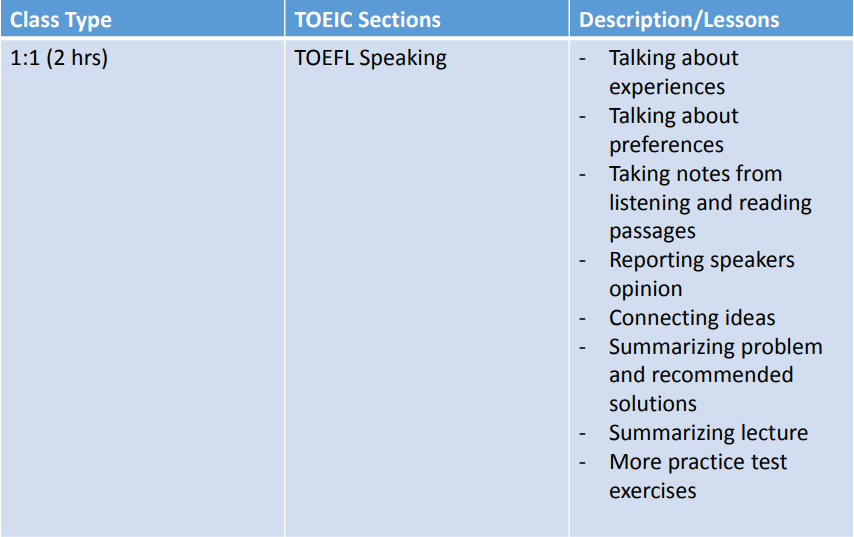
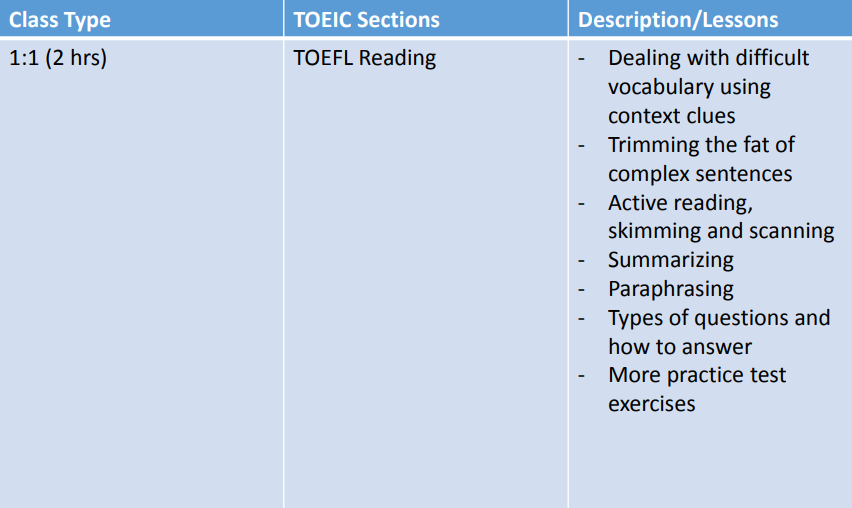
IDEA Programs
Success Starts With An IDEA
Level System
Start-Up learners cannot read or write in English. They may have limited oral proficiency in English.
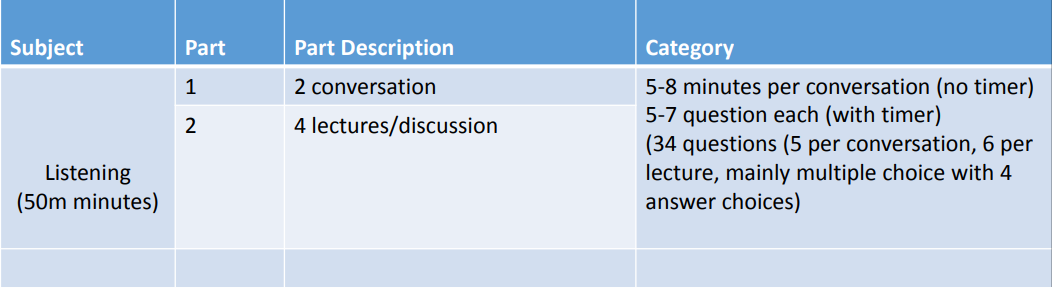
Listening
– Respond to simple questions such as personal information.
– Demonstrate understanding of familiar vocabulary through physical responses.
– Able to understand simple instructions.
Speaking
– Ask questions using a word or short phrases.
– Able to have basic conversation exchanges using learned phrases.
– Identify different objects and actions with one or two phrases.
– Able to answer simple questions with ‘Yes or No’ or one to two words.
Reading
– Able to read basic words and signs.
– Able to follow simple written instructions with pictures.
– Able to read phonological sounds to letters.
Writing
– Able to write personal information.
– Able to write words that were learned and used.
– Able to write familiar words and short phrases.
Basic learners have little or no ability to understand spoken and written English used in academic or social setting.
Listening
– Respond to simple requests.
– Appropriately respond to short warnings and commands.
– Demonstrate understanding of simple face to face conversation.
– Demonstrate understanding of simple words such as words that are used in everyday situations.
Speaking
– Make simple statements about everyday activities.
– Able to answer simple questions with short phrases.
– Engage in simple conversation but limited only with familiar phrases.
– Give simple commands and express caution using short phrases.
Reading
– Recognize personal information words in print.
– Able to follow step by step instructions.
– Read and understand simple sentences which is composed of words that were previously learned.
– Use familiar visual clues such as pictures, graphs and charts to predict the meaning.
Writing
– Legibly write print letters.
– Able to write familiar words.
– Write series of simple sentences about one topic.
– Able to fill out forms that require limited personal information.
Classic learners have limited ability to read and write in English. Can read familiar phrases and simple sentences but have limited understanding of connected prose and may need frequent re-reading.
Listening
– Able to appropriately respond to simple instructions and other non-classroom requests.
– Able to differentiate statements and questions based on grammatical structure and intonation patterns.
– Identify the main topic of the conversation.
– Recognize words that signal differences between present, past and future events.
Speaking
– Ask and answer simple questions related to basic needs.
– Able to have conversation on familiar topics.
– Give and ask for simple directions and instructions.
– Ask and give meaning of familiar words and expressions.
Reading
– Use context clues to understand the meaning of the new words.
– Able to read and understand simplified narrative paragraphs.
– Able to identify sequence of the events of a story.
– Identify the main idea of a brief passage.
Writing
– Able to write simple sentences and organize it into paragraphs.
– Able to fill out detailed personal information.
– Able to identify and write down the main information of the recorded passage.
– Able to identify capitalization, punctuation marks and incorrect spelling.
Learners function satisfactorily in the use of English in basic survival situation related to their needs.
Listening
– Differentiate formal and informal languages.
– Demonstrate understanding of the meaning of unfamiliar words based on context clues.
– Able to identify essential information just by listening passages.
Speaking
– Able to describe a topic related to daily lives.
– Able to prepare and deliver a short and simple oral presentation on familiar topics.
– Initiate and maintain simple conversation using appropriate formal and informal addresses.
– Give and ask for directions and able to make complex commands and warnings.
Reading
– Able to interpret simple narrative and descriptive passages using visual, graphic and textual cues.
– Skim for general meaning in short passages or paragraphs.
– Able to identify the main idea of the paragraph.
Writing
– Write short note or message including some supporting details.
– Able to write down familiar phrases transmitted orally.
– Write a paragraph that includes a topic sentence, supporting details and a conclusion.
– Able to edit spelling, capitalization, and basic grammatical form with some degree of accuracy.
Learners have the ability to speak in a simple manner using English commonly heard in routine academic and social setting.
Listening
– Demonstrate understanding of everyday conversations.
– Able to listen and record details.
– Able to identify main and supporting ideas just by listening.
– Detect the general mood of a story.
Speaking
– Engage in longer conversation whether be it familiar or unfamiliar topics.
– Ask and give clarification of previous utterances.
– Participate in face to face conversation on some topics beyond immediate survival needs such as personal histories and descriptions of people and places.
Reading
– Identify chronological order and simple transition in texts on familiar subjects.
– Able to draw conclusion on familiar topics.
– Determine connections between ideas within a passage by interpreting transitional words.
– Understand implied meaning in simple sentences.
Writing
– Take notes on both familiar and unfamiliar information which were transmitted orally.
– Produce short essays using simple transition words.
– Fill out increasingly complex papers, forms, questionnaires and surveys.
– Write a short e-mail or business letters.
Learners have enough ability in the use of English to function independently in most familiar situations.
Listening
– Identify key information/detail in a description.
– Respond to request for clarification and elaboration.
– Distinguish between facts and opinions in a conversation.
– Immediately detect mood changes and make predictions about what the speaker will say next.
Speaking
– Ask and make questions using complex sentences.
– Express opinions, arguments/disagreement, satisfaction/dissatisfaction.
– Provide detailed instruction.
– Produce statements, questions and commands in less familiar context with some details.
Reading
– Able to scan passages or forms to identify particular details.
– Identify facts and opinions in a text.
– Skim for main idea and scan for details in prose texts and documents.
– Interpret information in a text in order to answer questions.
Writing
– Able to find information and draw conclusion by reading different passages.
– Can write detailed message and information.
– Draft, organize, write and edit short paragraphs using the main idea and supporting details.
Learners have the ability to use English to meet most routine social and work-related demands with confidence, though not without instances of hesitations and circumlocutions.
Listening
– Respond to face to face conversation spoken at normal speed that include slang languages.
– Has adapt listening strategies that include both unfamiliar and familiar conversation.
– Identify accurate and applicable information from a complex passage.
Speaking
– Prepare and deliver a well-organized oral presentation on a general topic.
– Knows how to be flexible when talking in a different types of situations.
– Engage in complex conversation whether be it familiar or unfamiliar topic.
– Speak fluently in informal conversation on practical and social topics.
Reading
– Apply appropriate reading strategies for understanding unfamiliar content.
– Make judgment on the information that can be seen in the reading material.
– Interpret main ideas and key points from specialized materials.
– Evaluate information for accuracy and relevant purposes.
Writing
– Expand and combine simple sentences by adding modifying words, clause and phrases.
– Able to write detailed letters or messages with some degree of accuracy.
– Able to write summaries and paraphrase sentences of the reading materials.
– Write one to two descriptive and expository paragraph composition using correct punctuation and coherent organization.
Learners have the ability to use English to function effectively in familiar and unfamiliar social and work related situations with confidence.
Listening
– Understand conversation, lectures, discussion and speeches related to the field of interest.
– Determine the usefulness, bias, accuracy of the information presented orally.
– Listen selectively for words, phrases, or idea unite and other clues to infer meaning of the unknown words.
– Use context and work analysis skills to understand vocabulary and use multiple strategies to understand unfamiliar words.
Speaking
– Speak with fluency on specialized subject of interest.
– Engage in debate on organized or familiar topics.
– Prepare and deliver well-organized oral presentation on a specialized topic.
– Participate in casual, formal and extended conversation on practical and academic topics.
Reading
– Analyze author’s point of view.
– Determine meaning of increasingly complex passages by using contextual clues.
– Use background knowledge and linguistic contextual clues to understand the meaning of the unknown word.
– Accurately present, highlight and illustrate key points.
Writing
– Take note from full length formal presentation.
– Edit own and peer’s writing in terms of grammar, word choice, spelling, mechanics and sentence variety and organization.
– Use less common and idiomatic expression with occasional errors.
– Write composition with clear introduction, supporting details and conclusion.
Learners have the ability to use English to meet social, academic and vocational demands with confidence and success.
Listening
– Respond to topics beyond immediate survival needs such as news and events in the workplace and community.
– Reorganize and respond to idiomatic expression in a conversation.
– Recognize conversation openers/closures and polite expressions as used by the native speakers.
– Obtain detailed information in variety of context from conversation or broadcast.
Speaking
– Use a full range of pronunciation features with precision.
– Produce consistent accurate sentence structures.
– Know how to negotiate and compromise. Use persuasion in conversations.
– Clarify utterances by rewording or repeating in order to be understood by the general public.
Reading
– Distinguish, interpret and summarize descriptions and narrative topics.
– Knows how to use different reading strategies in order to understand different passages.
– Understand a variety of sentence patterns, new vocabulary and high frequency idioms.
– Take notes while reading and able to form opinions and conclusions.
Writing
– Write complex essays on a range of topics.
– Naturally and accurately use full range structures.
– Establish mood by choosing words that are appropriate for the situation.
– Able to distinguish literal from figurative languages.
Programs
ESL
Designed to improve fluency, precision, and communication skills to help achieve the confidence necessary for the English-speaking corporate world. This assures improvement on the macro skills: reading, writing, speaking, and listening while taking on key areas of business. This prepares you for more effective communication in presentations, negotiations, and meetings; as well as self-expression with increased poise and assertive tone.
Duration: 8 weeks~24 weeks
Class hours: 50 min per class, 10 min breaks in between
Start of class: Monday
Level: Start-Up~Extreme 3
Curriculum:
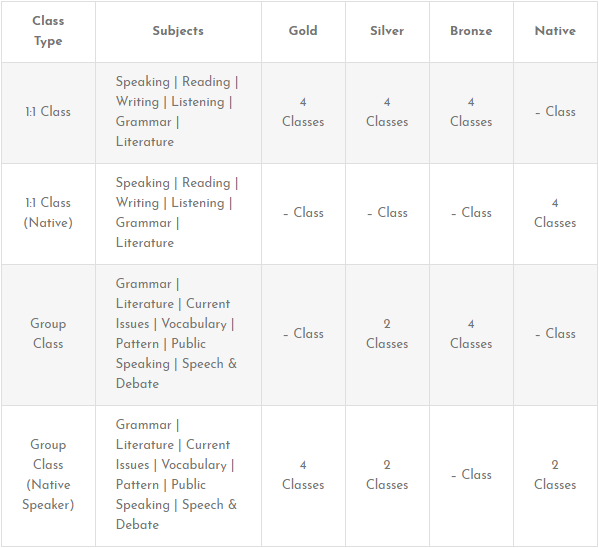
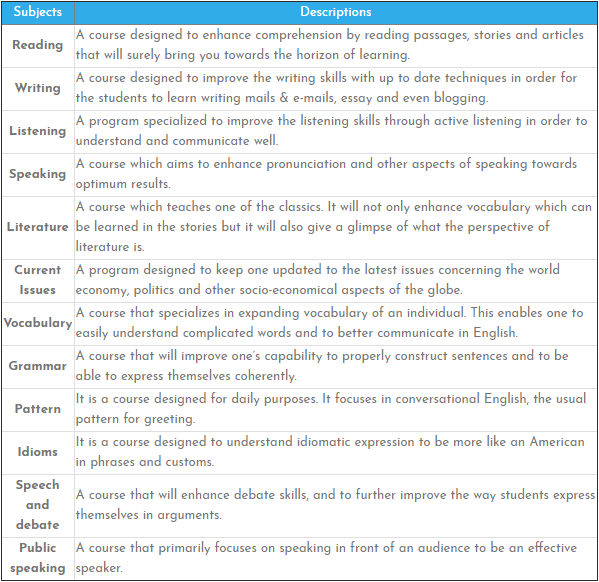
Description of the Subjects:
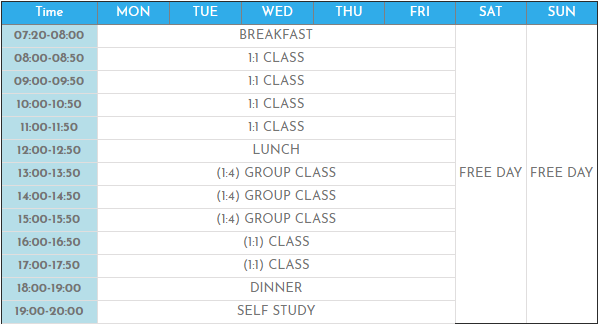
Class Schedule:
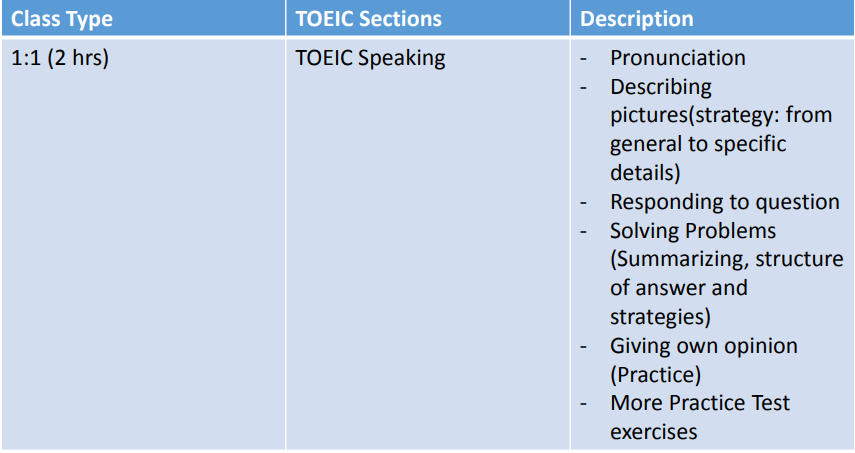
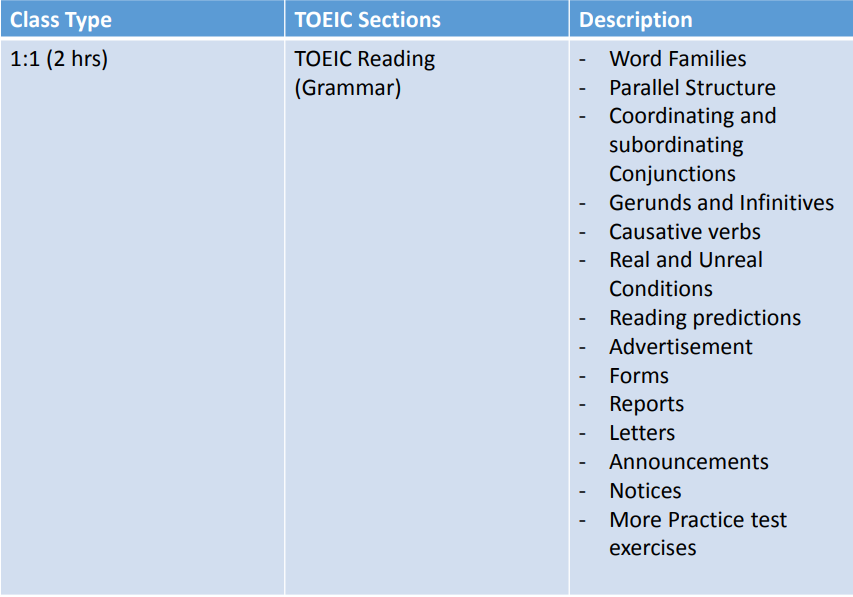
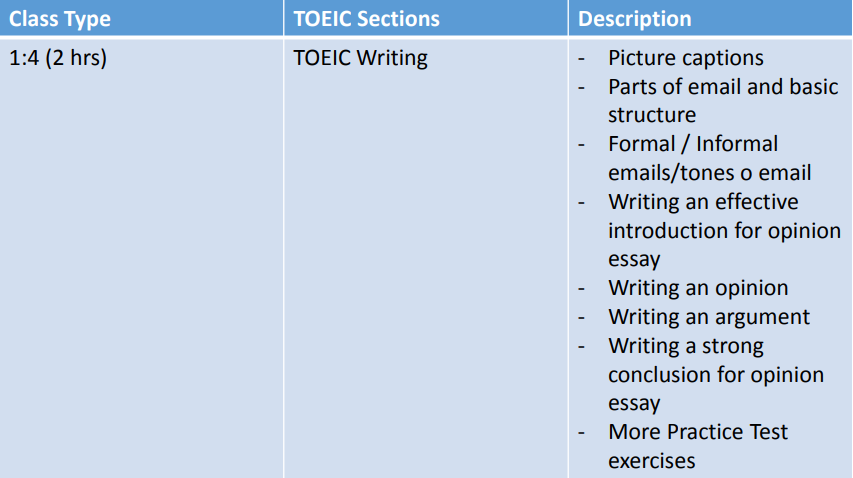
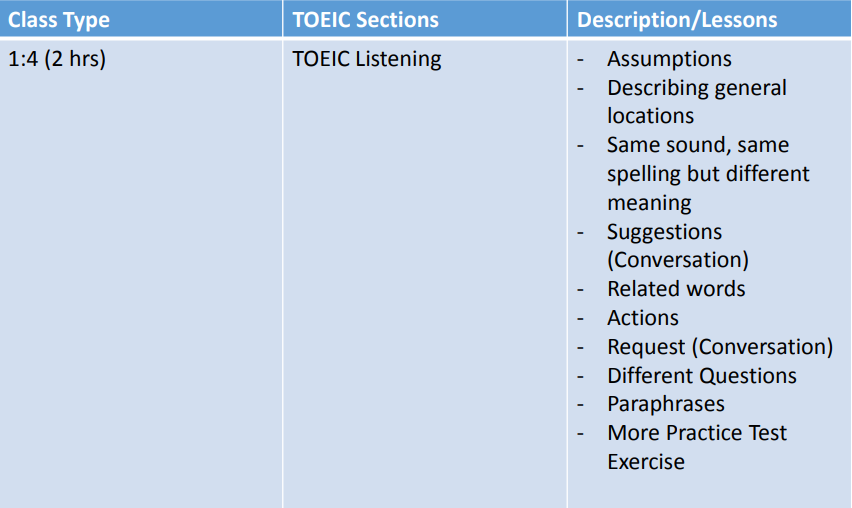
TOEIC
TOEIC – Test of English for International Communication. It has been used internationally as a standard assessment of English language proficiency. It has been developed to evaluate the English language skills of non-native speakers of English in the field of business.
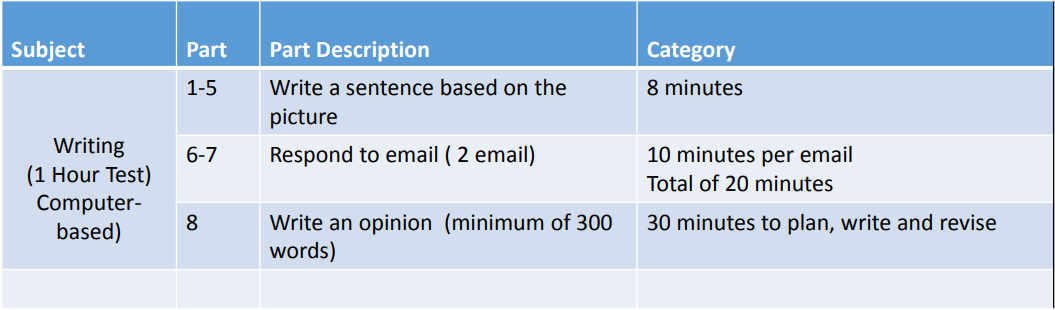
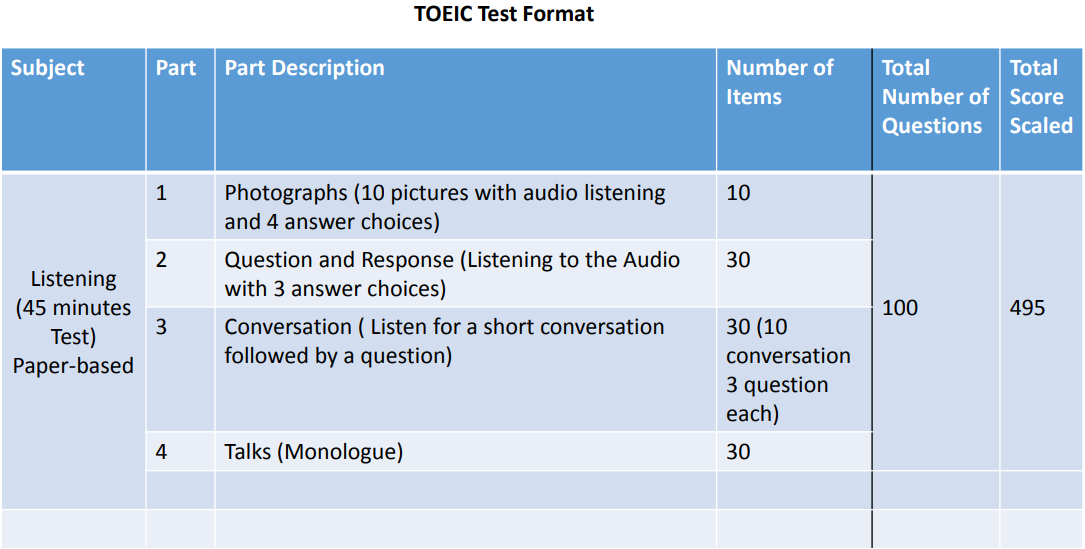
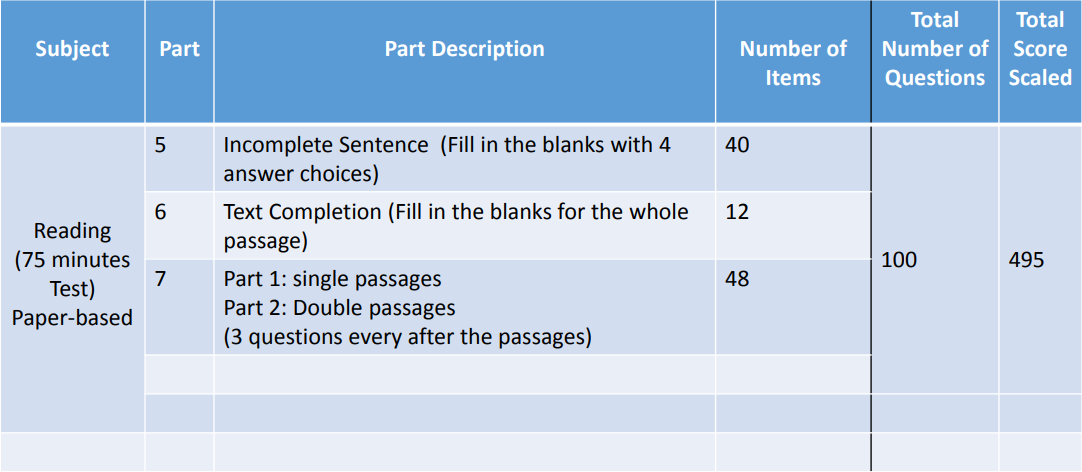
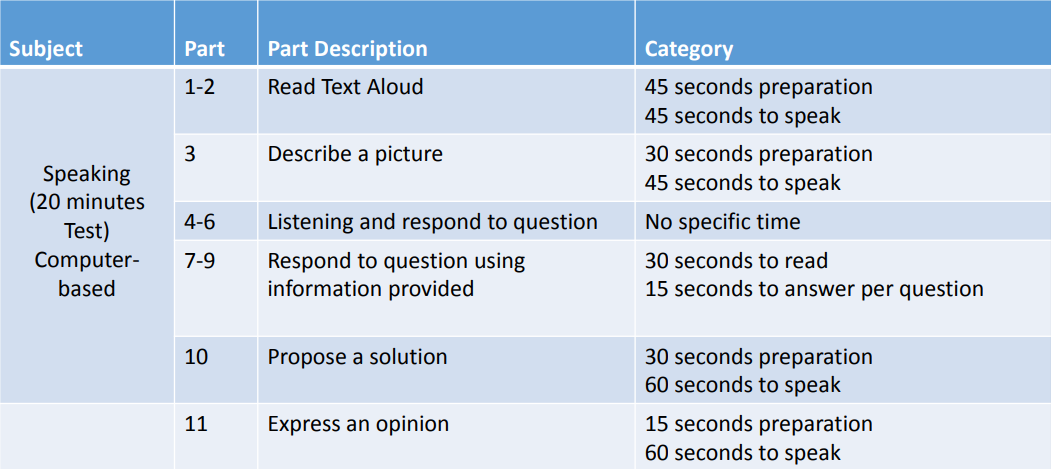
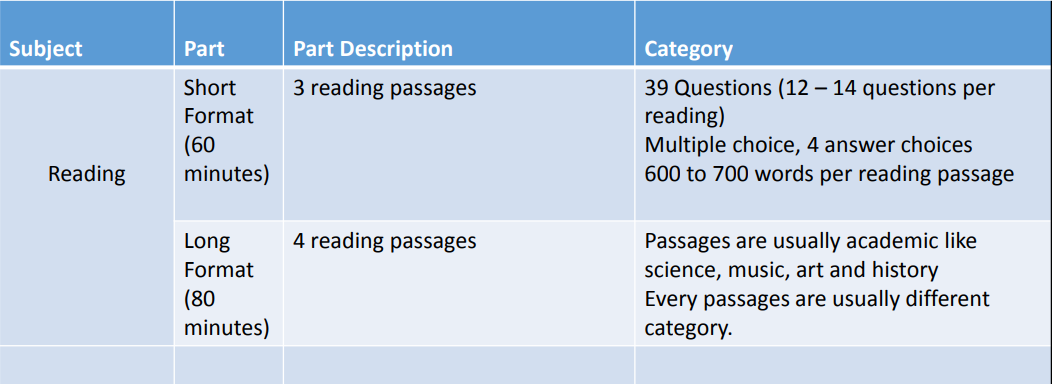
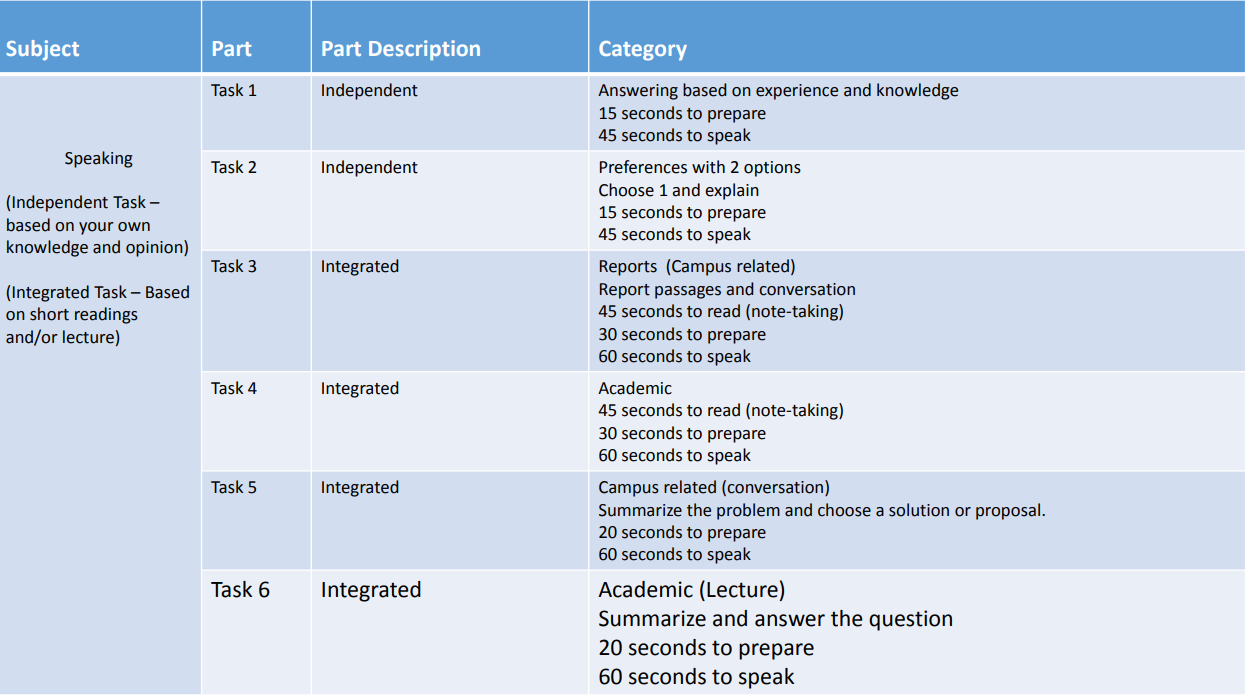
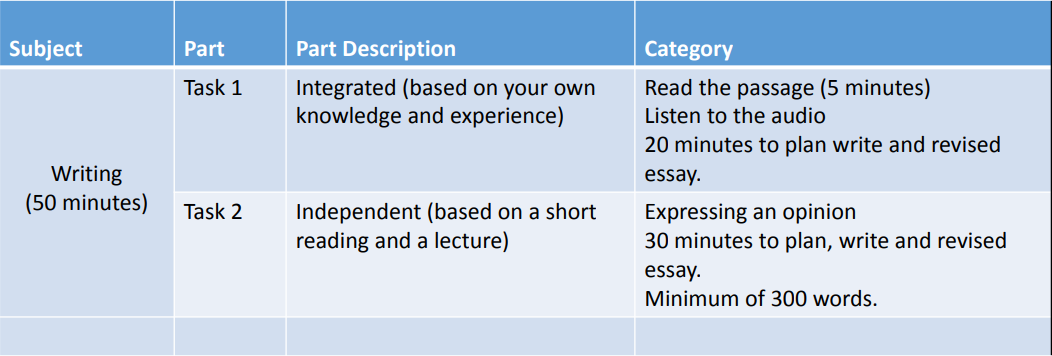
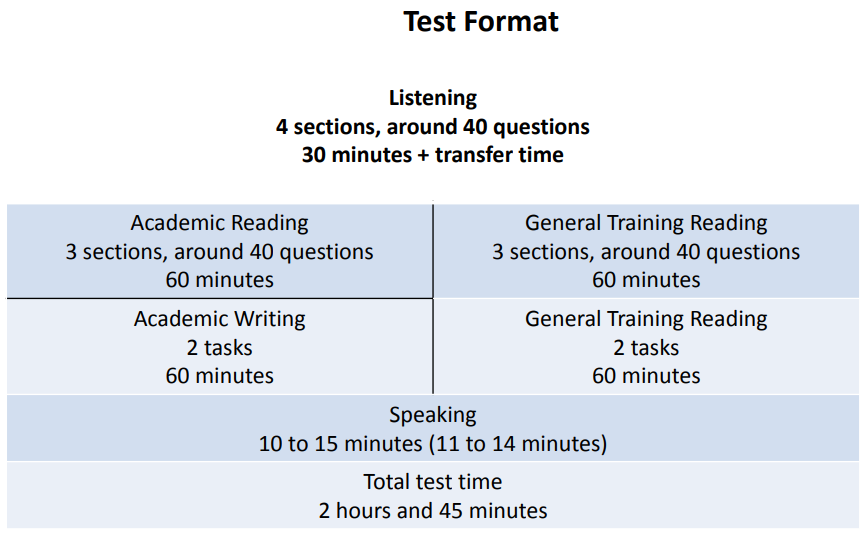
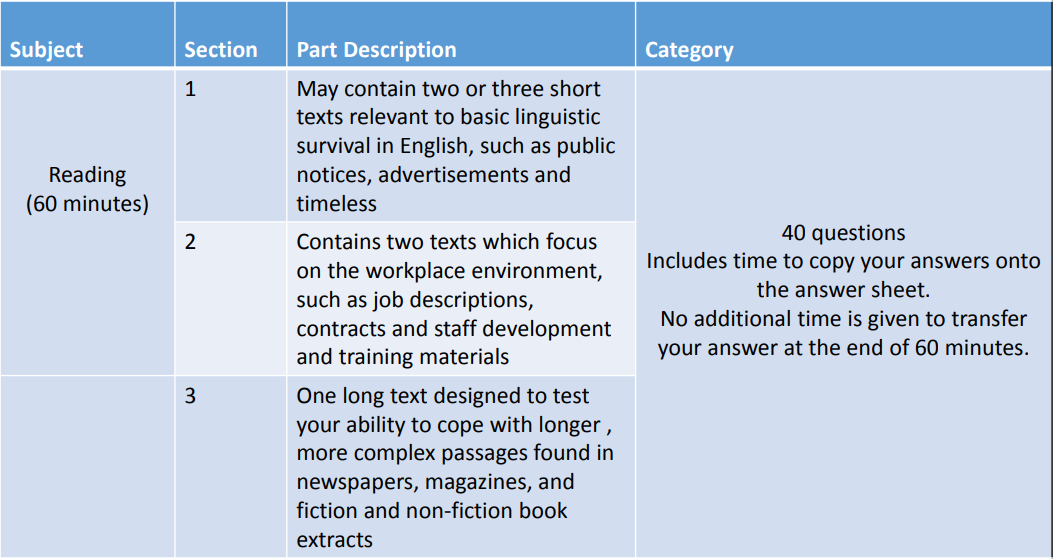
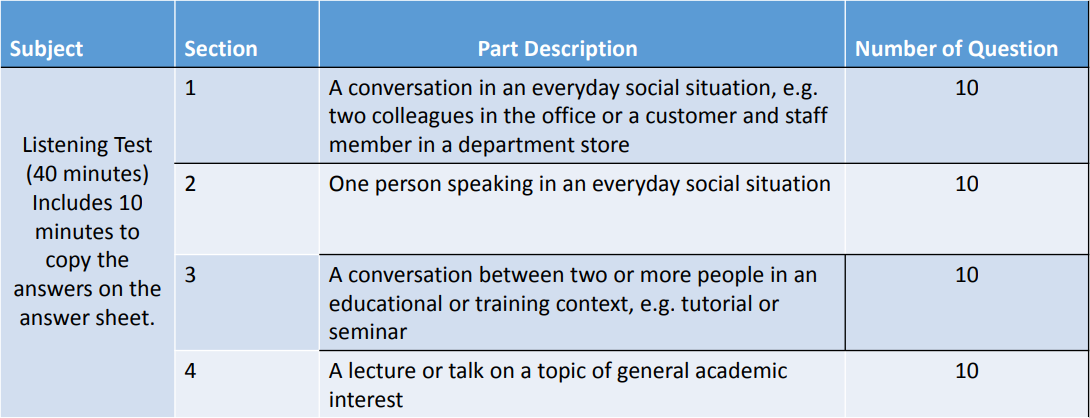
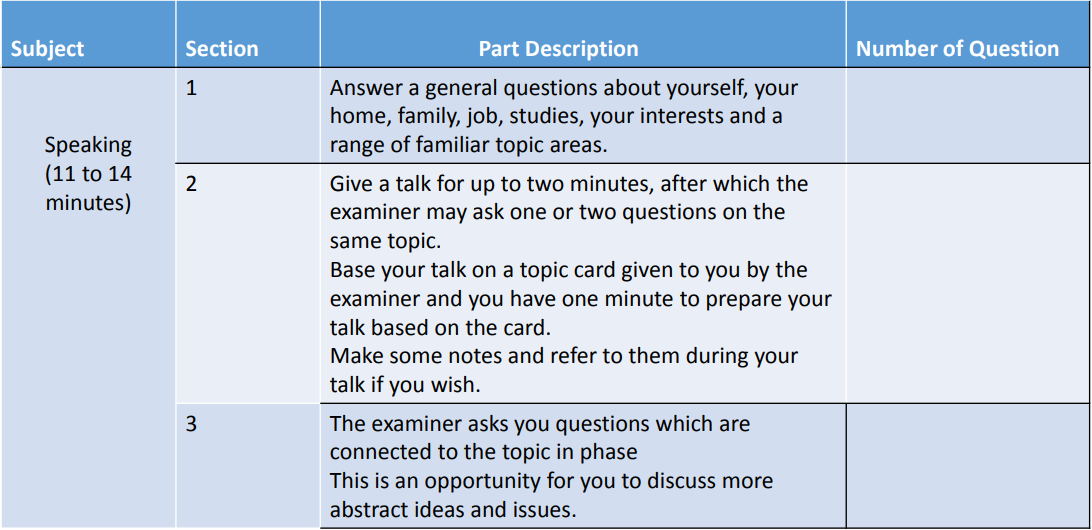
Test Structure and Timing for Listening and Reading
SP ( Secure Program) : Standard and most common form of the test. Administered direct by the TOEIC Steering Committee or their local representatives.
IP (Institutional Program): Generally used for assessment of new employees, as a placement test for in-company English lessons or for self-devekopment.
The TOEIC is offered worldwide and is generally available upon demand. The dates,time, and locations of the test sites are determined by the local TOEIC representatives.
Separate scores are given for the Listening Comprehension ( 5 to 495 scaled score ) and Reading ( 5 to 495 scaled score). These two sub-scores are added to arrive at the total score. The TOEIC score is represented on a scale of 10-990 and is based on the total number of correct answers.
TOEFL
TOEFL – Test of English as a Foreign Language
The TOEFL IBT test, delivered via internet, is an important part of your journey in an English – speaking country. The TOEFL IBT test measures your ability to understand English at the university level. And it evaluates how well you combine your listening , reading, speaking and writting skills to perform academic tasks.
Score requirements varies depending on the purpose of the examinee. Test Takers may take TOEFL IBT as many times as you wish to score to your satisfaction, but only once within 21 days. TOEFL Test scores are valid for (2) two years.
IELTS
EILTS – International English Language Testing System
This is a test designed to access the English language skills of non- English speaking students seeking to study in an English speaking country.
It is widely recognized as a reliable means of assessing whether candidates are ready to study or train in the medium of English. EILTS is owned by three partners. The university of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate, The British Council and IDP Education Australia (Through its subsidiary company IELTS Australia Pty Limited).
Two versions of the EILTS Test:
Academic Module: For students seeking entry to a university or institution of higher education offering degree and diploma.
General Training Module:For students seeking entry to a secondary school or to vocational training courses.